SWOT analysis is a strategy to examine strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for a business or an organization. This tool is not just limited to industries but is also applicable to communities, NGOs, etc. It gives insights about the competition, scope of improvement, ways to utilize opportunities, and prevention from possible risks.
It was first invented by Albert Humphrey in the 1960s. Slowly, after the years, it has become a widely used business tool.
What is SWOT analysis?
SWOT analysis revolves around 4 elements that depend upon the desired outcome. A few key people in the process or decision makers should first decide if the end goal is reachable or not. Afterward, SWOTs should be defined. This lays out the framework of things essential to achieve the objective.

- S (Strength): Features of a specific team or business form that give it benefits over other competitor industries. It can include people, technology, products, services, finances, marketing, and sales. Strength is helpful to resolve any risk or use any possibility.
- W (Weakness): Contrary to strength, it poses business aspects that are at a disadvantage over its competitors. It also means the inability to benefit from opportunities and susceptibility to dangers. It comprises multiple things like low-quality technology, poor finance, low employee morale, inefficient customer service, and sales.
- O (Opportunity): It is the possibility to make profits, sell, or expand the business. It can be any technological innovation that grows the sales of products or services. Additionally, opportunity can strengthen the brand’s reputation or image.
- T (Threats): These are the outer aspects causing trouble for the business. Multiple factors can induce threats:
- New competitor
- Robbery
- Conditional laws
- Reputation damaging elements
- Service or product-related issues
Different strategies resulting from SWOT
The above-mentioned elements can be matched and converted to form further techniques.
Growth
Opportunity when matched with strength can result in growth. In this process, you invest in those characteristics that boost your ability to perform the same task more often. It may involve hiring more workers or buying advanced machinery. The outcome is to constantly strengthen your competitive advantage.
Exterior development
It is the product of transforming threats into opportunities by using strengths. It can be achieved through publicity to acquire new customers and enriching services to broaden market reach.
Interior expansion
When weaknesses are converted to strengths they match an opportunity. It is all about expanding inner aspects to generate new capabilities. It can come in the form of employing new staff or training existing employees to cultivate advanced competencies or creating unique methods.
Continuity
When threats merged with weaknesses can formulate strategies for survival or continuation. It may involve changing the organizational structure, dissolving any unit, or making significant changes in the company.
Read more, about the top 3 business models to watch out for.
The step-by-step approach to a SWOT analysis
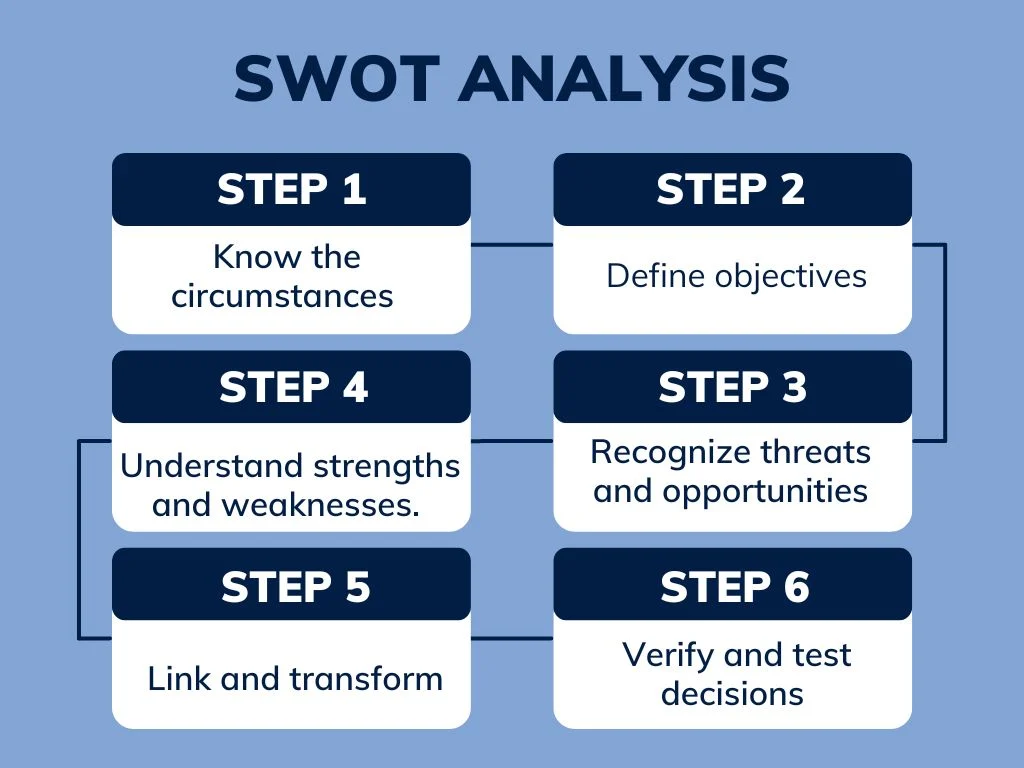
Know the circumstances
To begin with SWOT, one must define the context. The context gives the ability to evaluate and analyze the problems and elements so that they can be correctly set in the SWOT matrix. It generally includes:
- Goals, type of business or industry, and customers (existing and potential)
- Vision and mission statements of business
Objective
An ideal objective aids you in determining essential inputs for the SWOT analysis. Know the objective or purpose to elevate focus and get rid of unnecessary issues. Purpose can revolve around any function, such as marketing, invoicing, product development, etc. Furthermore, it helps with other things like forming new business units.
Recognize threats and opportunities
Opportunities and Threats are often presented when building a strategy in response to the changing world. Certain tools can be employed to determine the dangers and possibilities in the business environment.
- Market research
- Customer feedback
- Competitor analysis
- Employee feedback
Understand strengths and weaknesses
These are internal elements that can be controlled. Refer to the following tools to identify your positives and negatives:
- Process mapping: This is a flowchart that contains all the main elements involved in the business. It points out the strong points that can resolve the issue and the weaknesses that can affect it.
- What if: It promotes imagination and out-of-the-box ideas. It lays out the framework for issues that have not yet occurred. For example: what if we employ this particular technique, what if we address different customers, etc?
- Specific checklists: Prepare checklists for the main business functionalities. Consider, for instance, marketing, R&D, purchase, customer service, recruitment, etc.
Link and transform
- Linking involves matching the external factors (opportunities and threats) with the internal elements (strengths and weaknesses).
- Transforming deals with changing unfavorable conditions to favorable ones. Threats are converted into opportunities. Similarly, weaknesses are transformed into strengths.
Verify decisions
Decisions can often be subjective and need to be verified. The following areas should be checked:
- Efficiency
- Effectiveness
- Reliable actions
- Alignment of decisions with business culture
- Intended results
Deployment
Deploying strategies is a complete subject in its own right. Intent must be turned into action in your strategy.
- Convey your strategy to people for clarity, consistency, and simplicity.
- Implement it with the proper plan and execute it.
- Set some parameters and measure success.
If you want to learn more about any other business tool, please let us know in the comment section.