Internet of Things (IoT) is the latest term emerging from the outbreak of smart things. Simply put, it’s a process that allows communication between sensors and electronic instruments via the internet to ease our lives. It uses the internet and smart machines to offer creative solutions to diverse threats and problems associated with businesses, private industries, and governments across the globe. This article will explain the basic structure and top IoT application domains.
What is IoT?
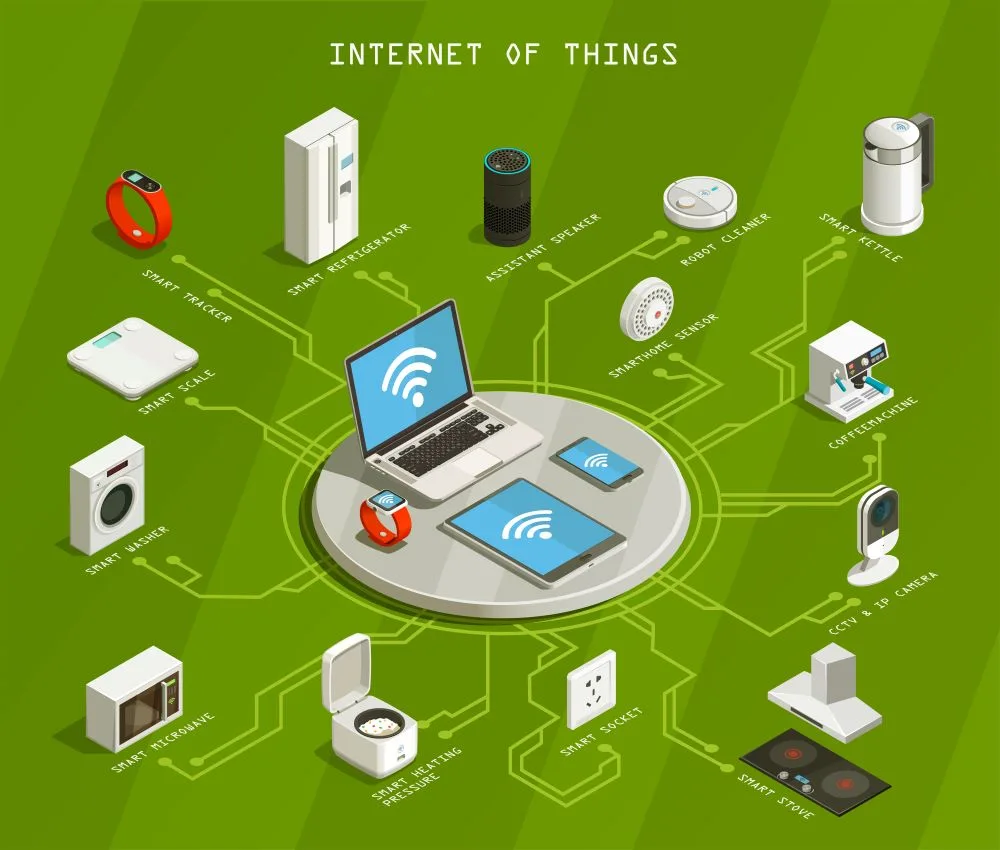
The Internet of Things is a distributed mesh of connected physical objects equipped with sensors, software, and other techniques for linking and exchanging data with other devices through the network. Material things can range from smartphones to home stuff. Below is the list of common IoT examples that we see in our everyday life:
- Connected cars, homes, cities, etc.
- Biometric scanners for cybersecurity
- Agricultural equipment
- Wireless trackers
- Smart industry devices
- High-speed net
- Logistic tracking and shipping containers
A typical IoT system comprises three phases: collection, transmission, and analysis of data, and for that, it needs three elements:
- Intelligent machines: These devices are selected based on their computing capacities. Examples include security cameras, a TV, workout supplies, etc. They gather data from user input, patterns, or their surroundings and transmit it to the cloud.
- Application: It includes services and software that integrate data from IoT devices. To make informed decisions, this data is analyzed with machine learning or artificial intelligence (AI). Decisions are communicated back to IoT devices, which smartly respond to inputs.
- GUI (graphical user interface): GUI is a means of managing IoT devices. For example, smart devices are manageable using mobile applications or websites.
The Impact of IoT
The fundamental purpose of IoT is to let people live and work more efficiently. In addition to reducing waste, it improves service delivery by reducing manufacturing and supply costs. Consequently, customers can transact with greater transparency and flexibility. Due to IoT, businesses have real-time access to what their systems are doing, from machines to supply chains and logistics.
Other technologies like edge computing, cloud computing, and machine learning allow physical things to collect and share data without relying on humans. Digital systems in today’s world can record, monitor, and modify interactions between connected objects.
IoT Structure
IoT structure/architecture consists of four segments.
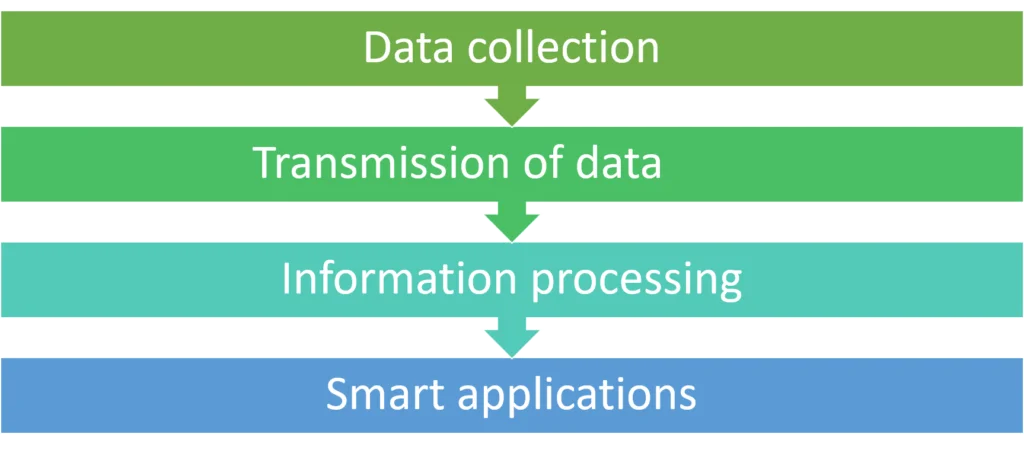
Data Collection
Sensors and actuators are the primary devices that control (actuator) or monitor (sensors) some approaches or processes in the IoT. Sensors turn external information into data for analysis. The actuator, on the other hand, influences the physical world. For example, they have the ability to stop or adjust the operations in the industry. This makes it possible to get the required observations for further investigation.
Sensors collect information about a method/operation or an environmental condition, like humidity, temperature, etc. When a sensor detects a situation that requires immediate attention, an actuator responds immediately.
Transmission of Data
This phase focuses on network gateways and DAS (data acquisition system). DAS gathers raw data from sensors and transmits it into digital format. This data is then aggregated and formatted through wireless or wired WANs before sharing via internet gateways.
This is important in the case of large volumes of data. Typically, a factory has thousands of sensors that gather a large amount of data, which is then filtered and optimized for smooth transmission. Advanced gateways provide connectivity for Sensor networks and protect against malware.
Information Processing
In this stage, digitized and aggregated data volumes are reduced before being put into the cloud or data center. As part of the pre-processing, the edge device may conduct some analysis. At this point, machine learning can provide feedback to the system and improve it on an ongoing basis. Accordingly, it avoids waiting for instructions from the corporate data center.
Smart Applications
Here, an effective IT system comes into the picture. IoT data is gathered in a cloud or data center where multiple sensors are integrated to provide a clear view of the overall system. Additionally, it offers actionable insights to both IT and business managers. IoT data analysis can determine significant trends, patterns, and abnormalities in companies operating across geographies. Also included is storing the data in a data warehouse for archival and research purposes.
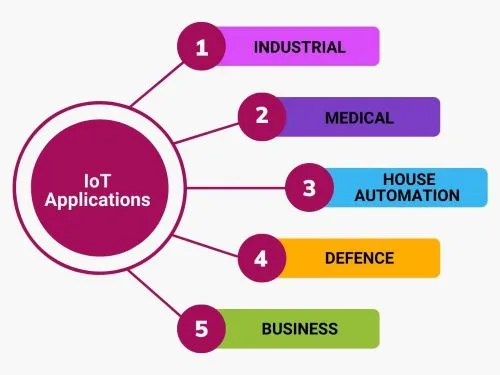
IoT Application Domains
The following image illustrates the significant IoT domains.
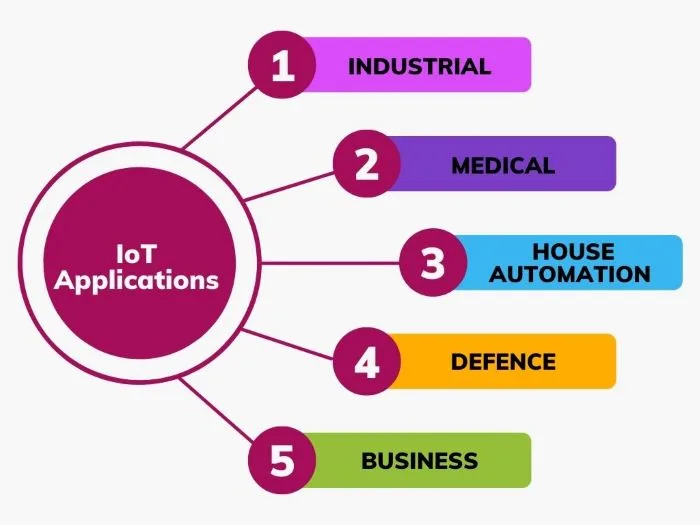
Industrial
IoT implemented in industry 4.0 is popularly known as IIoT (industrial Internet of Things). It has expanded its scope into a variety of features.
Read more about how to convert small and medium-scale enterprises into Industry 4.0.
Quality Control (QC)
IIoT monitors the quality of any product at each stage, from procurement to the final delivery. Moreover, it corrects and prevents risks from occurring in the product lifecycle. With IIoT, industries can assure defect-free products, optimize processes, and maintain the proper functionality.
Refer to our article on the 15 most valuable terms to understand ISO 9001:2015 to learn about industry compliance and process optimization.
Automation
Automating devices/equipment enables a centralized system to observe and control all operations in the company. It can examine all the plants at different sites through software and machinery. This is highly crucial while making data-based decisions.
Refer to our article on how to get started with Robotic Process Automation in 6 easy steps if you want to learn about RPA.
Improvement Execution
IIoT allows easy assessment of the operation, data analysis, and remote adjustments (if any) in the approach. This facilitates the execution of those changes in a timely manner. Therefore, it ensures smooth improvements.
Maintenance Analysis using IoT
Sensors installed on machines and operating platforms send alerts in the case of emerging risks. Moreover, they inform about the necessary maintenance that can prevent a machine failure or downtime. Usually, sensors transmit data to platforms, which analyze it in real-time and perform algorithms that can alert operators when operating conditions exceed normal limits.
Supply Chain Management
Due to IIoT, it is possible to track the in-transit information related to the supply chain. This approach identifies potential improvements and pinpoints the problems that contribute to inefficient or unprofitable process flows.
It also monitors the status of inventories.
Environment Safety
An IIoT machine can generate real-time data about the state of the plant. Monitoring equipment damage, air quality at a facility, and other such things can prevent hazardous scenarios that threaten workers.
Medical
IoT application domains in the medical field exist in several ways, such as tracking how many patients are in a hospital, receiving the correct medicine for a patient, and monitoring their health at a distance, also known as Telemedicine. Patient surveillance is observed through sensors fitted on Bluetooth devices and toothbrushes. This will enhance the monitoring and measurement techniques for vital body functions such as blood pressure, temperature, heart rate, blood glucose, cholesterol levels, and so on.
When IoT is integrated with data analytics, it forms digital twins. This can create a virtual replica of the human body that provides real-time analysis. Healthcare professionals can use it to do analysis, simulate different conditions and diagnose patients with maximum accuracy.
Approximately, 8.6 million Europeans used connected healthcare solutions in 2021, according to Berg Insight.
Building and House Automation
In smart home automation, users can manage wireless instruments from anywhere. House automation involves a few examples:
- Air composition sensors
- Fire detection
- Motion sensors
- Access control
- Sound sensors
Smart cities can use IoT to create intelligent transportation systems, buildings, congestion management, waste management, lighting, parking, and urban maps. Monitoring may include a variety of features, such as:
- Observing vibrations as well as the materials used for bridges and buildings
- Monitoring parking spaces within a city
- Detecting pedestrians and vehicle levels
- Setting up sound monitoring devices in sensitive areas
IoT applications have a wide scope in smart living as well. The launch of IKEA’s Matter-ready hub is a substantial step toward the company’s smart home ambitions.
IoT in Defense
With IoT defense, proven and verified applications can monetize intelligence ideally and amplify military forces in the technology age. Refer to the below areas that cover defense applications:
- Health surveillance of fighters working on the battlefield
- Fleet management of equipment and vehicles
- Battlefield survey using connected cameras and airborne drones
- Transportation using intelligent software and sensors
- Target detection using AI
- Inventory management
IoT has potential in other domains like agriculture, logistics, environment, etc. Its research and development arena includes a broad array of activities. It should resolve several privacy and security issues also.
Over the next few years, IoT will evolve further, requiring more innovative approaches in software engineering, systems engineering, project management, and other disciplines.


Very informative content
Thanks a lot for posting
Thank you, Sitesh!
[…] As technology evolves rapidly, semiconductor companies have a vast scope for opportunities to profit. Chip demand will surge in the near future due to 5G, AI, cloud computing, electric vehicles, and the Internet of Things. […]
[…] It is expected to be the communication hub that connects virtual reality, autonomous vehicles, IoT, and many other emerging […]
[…] individuals can verify, trace, and control their personal identities. Blockchain combined with IoT can even raise this bar higher with the integration of smart […]
[…] techniques can be applied to various ecosystems. For instance, consider IoT, mobiles, and […]
[…] have briefed about IIoT (Industrial internet of things) in the article top 5 IoT application domains. This one will cover the trends and principles of industry […]
[…] home, logistics, etc. When combined with the latest trends, such as artificial intelligence, IoT, etc., automation can yield magical […]
[…] There has been a lot of buzz around it since then. Smart cities are modern towns that combine IoT devices and ICT (information and communication technology) to connect with citizens, increase […]
[…] the integration of IoT and smart cities, data from localities, hospitals, banks, governments, networks, climate, etc., can […]
[…] Internet of things (IoT) has taken our world by storm. It is the basis of what is known as the intelligent industrial […]
[…] prominent field of IoT (Internet of things) combines smart entities into the internet to provide value to customers. Smart contracts when […]
Hello, thank you for the great blog today 샌즈카지노
Thank you!