Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning “change for the better,” is a principle of continuous improvement that has been widely adopted in businesses. It is about making small, incremental changes to processes, systems, and behaviors to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance quality.
Implementing Kaizen ideas is creating a culture of continuous improvement within a company. This means encouraging employees at all levels to find growth opportunities. It also involves providing the necessary support, resources, and training to help employees determine and execute changes effectively.
Kaizen increases efficiency. Organizations can facilitate their functions and attain great productivity. This leads to cost savings allowing organizations to deliver products and services quickly and effectively. It’s a powerful tool for companies looking to enhance their performance and achieve long-term success. Let us discover practical kaizen ideas to implement in a company.
Gemba
Gemba is a Japanese term that means “improvement at the workplace.” It emphasizes the importance of making continuous improvements directly at the place where work is done. Gemba refers to the location where value is created, whether it’s a factory floor, a sales office, or a customer service center.

Vital points of Gemba Kaizen include:
Respect for people
It recognizes that the people closest to the work are the ones best suited to identify opportunities for improvement. It collaborates with all employees appreciating their mastery, understanding, and expertise.
Continuous improvement
It is based on the idea that improvement is never-ending. It boosts companies to look for better ways of doing things, even if current methods are efficient.
Standardization
Standardizing ensures that improvements are sustainable and can be replicated across various company parts.
Visual management
It facilitates the use of visual tools, such as kanban boards and process maps, to make problems and opportunities for improvement more visible.
Waste reduction
It focuses on eliminating waste in all its forms, including excess inventory, unnecessary processing, and defects.
Here are some examples of how Gemba Kaizen ideas can be executed in different departments:
- Production: In this scenario, Gemba Kaizen could be used to regularly review and improve manufacturing strategies to grow efficiency, minimize faults, and enhance safety.
- Sales: Gemba analyzes the sales cycle from lead generation to closing deals and identifies areas where the process can be streamlined to increase sales.
- Customer service: Gemba in customer service involves checking customer feedback and call data to determine common issues or pain points and implementing changes to improve the customer experience.
Read more, how to distinguish between inventory and stocks.
5S System
The 5S system is a methodology focused on organizing and optimizing the workplace for efficiency and effectiveness. Each “S” stands for a specific step in the process: Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. Here’s an overview of each step and its benefits, along with practical tips for implementation:
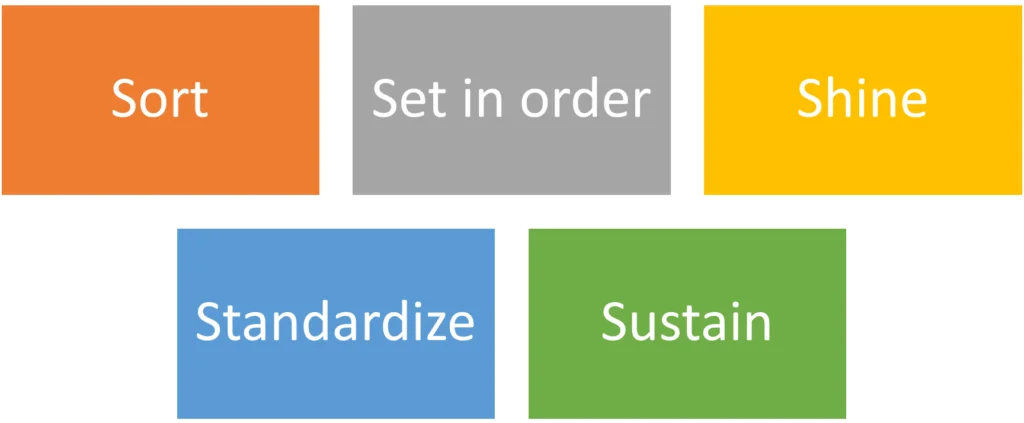
- Sort (Seiri): It sorts the required things and clears the clutter from the workspace. It removes mess, allows easier access to necessary items, and increases safety. Perform regular audits of the workspace, categorize items into necessary and unnecessary, scrap unrequired things, and manage a system to prevent clutter buildup.
- Set in order (Seiton): It defines a specific place for each item for better accessibility. It enhances efficiency, lessens search time, and grows productivity. Use labels and signs to identify item locations, use shadow boards or tool cribs to store tools, and set a system for returning items to their designated places after use.
- Shine (Seiso): This step thoroughly cleans the workspace and equipment. It maintains cleanliness, lowers the risk of accidents, improves equipment lifespan, and boosts employee morale. Develop a schedule, assign cleaning responsibilities, provide required tools and materials, and inspect the workspace for cleanliness.
- Standardize (Seiketsu): Standardization involves creating and implementing standardized work practices to maintain the previous improvements. It can achieve consistency in practices, easier training of new employees, sustained improvements, and improved efficiency. Develop standard operating procedures (SOPs) for each 5S step, provide training to employees, and regularly audit the workspace to ensure compliance.
- Sustain (Shitsuke): This involves creating a culture of continuous improvement and ensuring that they are deep-rooted in the organization’s culture. Conduct regular audits, provide training and support to employees, and reward them for their contributions.
Kaizen Events
Kaizen events, also known as Kaizen blitz or Kaizen bursts, are focused, short-term projects aimed at making significant changes in a specific area of a company. These events typically last from a few days to a few weeks and involve a cross-functional team working together to identify, analyze, and implement changes.

Regular Kaizen ideas involves incremental improvements often implemented as part of daily routine, Kaizen events are more structured and intensive, with a specific goal and timeline.
These are designed to achieve rapid upgrades in areas such as quality, productivity, and efficiency. They often use tools and techniques such as value stream mapping, 5S, and root cause analysis to eliminate waste, streamline processes, and modify overall performance.
By standardizing tools and procedures, the company may reduce setup times by 50%, leading to increased productivity and lower costs.
Overall, Kaizen events are strategic drivers for making crucial improvements in a short amount of time.
Also read, how to develop Agile business.
Visual management
It is instrumental in improving communication, enhancing efficiency, and promoting a culture of continuous improvement in the company. Visual management uses visual cues such as charts, graphs, and boards to communicate data quickly and effectively, making it easier to understand complex processes.

Visual tools such as Kanban boards, can enable teams to visualize their workflow, track progress, and recognize bottlenecks or inefficiencies. This boosts collaboration. Kanban boards can be useful in:
- Production: To visualize the production process, track work-in-progress, and identify areas for improvement in workflow efficiency.
- Inventory Management: Visual controls such as color-coded inventory tags or bins can identify inventory levels and reduce excess inventory.
- Project Management: Gantt charts or task boards can visualize project timelines, track progress, and identify potential delays or bottlenecks.
- Quality Control: Tools such as Pareto charts or control charts can monitor quality metrics and spot trends or patterns that may indicate areas for improvement.
- Safety: Visual cues such as safety signs, labels, and color-coded floor markings can communicate safety procedures and hazards, ensuring a safe work environment for employees.
Continuous Training and Education
These are essential for sustaining Kaizen efforts and ensuring employee engagement. Employees can deepen their understanding of Kaizen principles and techniques, stay updated on best practices, and develop the necessary skills to implement improvements effectively.
- Skill Development: Problem-solving, data analysis, and knowledge of lean principles and tools.
- Employee Engagement: Active participation in Kaizen activities.
- Sustained Improvement: Companies can sustain their improvement efforts over the long term by regularly reinforcing the principles of Kaizen and providing opportunities for skill development.
Training can take the following forms:
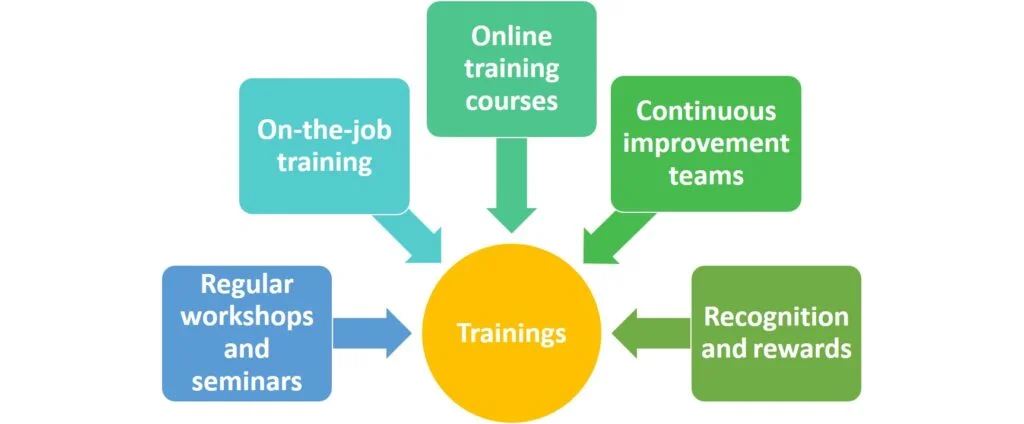
Overall, continuous training and education are essential for sustaining Kaizen efforts and ensuring that companies continue to improve and innovate over time.
Cross-Functional Teams
Cross-functional teams are groups of employees from different functional areas of an organization who come together to work on a specific project or goal. These can have several benefits:
Diverse Perspectives
Cross-functional groups have people with various skills, knowledge, and perspectives. This can bring out innovative solutions to problems.
Faster Decision-Making
These teams can make quick decisions as they have access to a wider range of expertise and information.
Improved Communication
Working in a cross-functional team encourages communication and collaboration between departments. This can lead to better coordination and alignment of efforts.
Better Problem-Solving
These teams are better equipped to solve complex problems that require input from multiple disciplines. Team members can develop more comprehensive solutions By pooling their knowledge and resources.
Increased Ownership
When employees from different departments are involved in a project, they are more likely to take ownership of its success, leading to greater accountability and commitment.
Tips for creating effective cross-functional teams:
- Clearly Define Goals and Roles: Ensure that all team members understand the goals of the project and their roles within the team. This helps prevent confusion and ensures everyone is working towards the same objectives.
Learn more, how to set and track Smart Goals.
- Establish Strong Leadership: Appoint a leader or facilitator for the team who can provide direction, resolve conflicts, and keep the team focused on the goal.
- Promote Open Communication: Encourage team members to communicate openly and create a supportive environment where everyone feels comfortable sharing their ideas and opinions.
- Provide Adequate Resources: Ensure the team has access to the resources they need to complete the project, whether it’s information, tools, or support from management.
- Set Clear Expectations: Establish clear milestones and deadlines for a project and regularly review progress to check if the team is on track.
- Celebrate Successes: Acknowledge and celebrate the achievements to keep morale high and motivation levels up.
Supplier Relationship Improvement
Strong supplier relationships can improve quality, reduce costs, increase efficiency, and enhance innovation. Here are some key reasons why building strong supplier relationships is crucial for continuous improvement:
- Quality Improvement: Collaborating closely with suppliers can improve better quality control and assurance processes, resulting in higher-quality products or services.
- Cost Reduction: Strong supplier relationships can help with cost reductions through improved efficiency, better pricing agreements, and reduced waste in the supply chain.
- Innovation: Suppliers can provide valuable insights and innovative ideas that can help improve products, processes, and services.
- Supply Chain Resilience: These can help build a more resilient supply chain capable of responding to disruptions and changes in the market.
- Mutual Benefit: Building good relationships with suppliers grows mutual trust and respect, creating a win-win situation for both parties.
To collaborate with suppliers and implement Kaizen ideas in the supply chain, consider the following ideas:
- Supplier Collaboration Meetings: Hold regular meetings with key suppliers to discuss opportunities for improvement, share best practices, and address any issues that may arise.
- Joint Kaizen Events: Collaborate with suppliers to identify and implement Kaizen projects that benefit both parties, such as improving delivery times, reducing defects, or optimizing inventory levels.
- Supplier Development Programs: Provide training and support to suppliers to help them implement Kaizen ideas in their operations, which can lead to improvements throughout the supply chain.
- Performance Measurement and Feedback: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) for suppliers and provide regular feedback on their performance, highlighting areas for improvement and recognizing achievements.
- Long-Term Partnerships: Build long-term partnerships with suppliers based on trust, transparency, and mutual benefit rather than focusing solely on short-term cost savings.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Using data to drive Kaizen ideas and measure their impact is crucial for several reasons:
Objective Decision-Making
Data provides an objective basis for decision-making, helping teams prioritize improvement opportunities based on their potential impact.
Identifying Root Causes
Data analysis can help teams identify the root causes of problems, allowing them to implement more effective solutions.
Measuring Progress
Data allows teams to track their progress over time, ensuring that improvements are sustained and that the desired outcomes are achieved.
Demonstrating ROI
Data helps demonstrate Kaizen initiatives’ return on investment (ROI), making it easier to secure resources and support for future projects.
Tips for collecting and analyzing data to identify improvement opportunities include:
- Define Key Metrics: Spot key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to the Kaizen initiative’s goals. These could include metrics such as cycle time, defect rate, or customer satisfaction.
- Collect Relevant Data: Collect data relevant to the KPIs identified, ensuring that it is accurate, timely, and complete.
- Use Visual Tools: Use visual tools such as charts, graphs, and dashboards to analyze data and identify trends or patterns that may indicate areas for improvement.
- Involve Employees: Involve employees in the data collection and analysis process, as they often have valuable insights and knowledge about the processes being analyzed.
- Prioritize Improvement Opportunities: Use data to prioritize improvement opportunities based on their potential impact and feasibility of implementation.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor and evaluate the impact of improvement efforts, using data to adjust strategies as needed to ensure success.
Leadership efforts
The role of leadership in supporting and sustaining Kaizen ideas is critical to the success of continuous improvement initiatives. Here are some ways in which leaders can support and sustain Kaizen efforts:

Setting Clear Expectations
Leaders should communicate the value of continuous improvement and set clear expectations for employees to actively participate in Kaizen activities.
Providing Resources
Leaders should provide the necessary resources, such as training, tools, and support, to enable employees to participate effectively in Kaizen efforts.
Removing Barriers
Leaders should identify and remove any barriers or obstacles that may hinder the implementation of Kaizen ideas, such as outdated policies or lack of support from other departments.
Leading by Example
Leaders should lead by example and actively participate in Kaizen activities, demonstrating their commitment to continuous improvement.
Recognizing and Rewarding Progress
Leaders should recognize and reward employees for their contributions to Kaizen’s efforts, reinforcing a culture of continuous improvement.
Monitoring Progress
Leaders should regularly monitor the progress of Kaizen ideas and provide feedback and guidance to ensure that they stay on track and achieve their goals.
By actively supporting and demonstrating their commitment to continuous improvement, leaders can help sustain Kaizen ideas and drive lasting change within the organization.