Product marketing is the process of selling products by positioning them in the market, crafting key messages, building customer personas, and improving them with competitive intelligence. It is one of the rapidly evolving sectors in product lifecycle management (PLM). This role collaborates with marketing, sales, product, and customer success. Each type of business, such as B2B and B2C, has a different product marketing strategy. In this article, we will understand some core concepts related to product marketing.
What is product marketing?
Product marketing is a process of conveying a product’s unique selling proposition to its customers. The availability of this branch depends on the company’s size, product market, sales volume, and competitiveness. This field is responsible for the following:
- Identifying customer needs
- Collaborating with internal stakeholders
- Crafting a go-to-market strategy
- Product positioning
- Helping with gaining new customers and strengthening relationships with old customers
- Communicating with customers to provide the best value and strengthen the brand’s image

Difference between product marketing and product management
Product management designs and builds products, and product marketing sells these products to customers. Refer to some of the key differences between them:
| Product Marketing | Product Management |
| Communicates everything about a product by simplifying complex info | Defines a product |
| Positions product in the market | Designs product roadmap and vision |
| Conveys core messages of the improvements or updates made in the products | Recognizes customer pain points and refine product needs |
| Manages product acquisition | Provides technical data to product marketing |
What are the famous 4 Ps of product marketing
The 4 Ps, including place, product, promotion, and price, are the pillars of the product marketing framework. These factors were introduced in the 19th century and, hence, are a part of even conventional marketing. These pillars, also known as the marketing mix, extended its capacity to include process, people, and physical evidence.
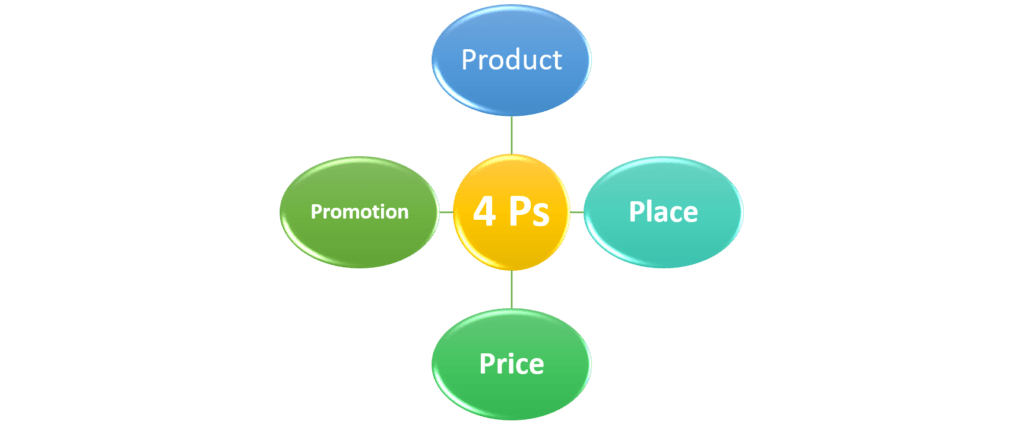
Product
Marketing personnel should be able to define the product and explain its specifications to the customer.
The product idea will then help create a marketing campaign. What are the product specifications? What is the USP of the product? How will it solve customer problems? How does it differ from the competition? How will it serve the customers even if it’s a totally new product?
Product marketing should answer all the questions related to the product lifecycle. The associated business should have all the solutions in place to tackle any query occurring at every step of the product lifecycle.
The type of product decides its pricing, market, and subsequent promotion. Several products have accomplished a lot despite being unique. For example, OpenAI developed ChatGPT in 2022, which can create content, write programs, and solve numerous complexities. This is almost a miracle in human history. Since its launch, OpenAI has generated billions of dollars in revenue.
Place
Place specifies the product’s availability online and offline. It is a means of displaying products in particular stores or places to get the best profits. It also focuses on promoting products or solutions at the right time, at the right location, and to the right audience.
Read more, how to build a profitable business.
Price
Price determines the real and perceived worth of a product. Marketers decide the approximate price, which consists of shipping costs, discounts, market demands, and retail value.
Promotion
Promotion is a mix of advertising, social media strategy, and public relations to spread the word about a product. It communicates the product’s needs, working, and costing to consumers. Promotion can be done online and offline. Marketers work diligently to reach their targeted audience through promotion and product placement.
Core functions of Product marketing
Product positioning
It specifies a product’s position in the market by highlighting its unique selling proposition (USP) and superiority. This is crucial as it sets a unique identity of the product over its competition. Consumers will understand the actual value of the product. It makes buying and selling easier. Product positioning creates a product’s story with authoritative content and creative visuals.
Strategy to design an effective product positioning
- Know your market: Categorize demographic trends, including age, gender, employment, etc., and technology trends, like AI, IoT, and many others. Analyze rules concerning privacy, compliance, and rights. Study the competition, economic factors, and potential future uncertainties. Understand the sentiments of your audience and be transparent about your offerings.
- Get to know your customers: Understanding the customer requirements using surveys, market research, and social media is crucial.
- Be aware of the competition: Competition can help you compare your products’ strengths, pricing, specifications, and strategies with those of your competitors. This can clearly define the way to market your product positioning.
- Write a positioning statement: Draft a brief statement by identifying gaps, patterns, and USPs of your product or services. Clearly write about specific users, their requirements, your product, and its benefits. Refer to this example from Wistia: “We are Wistia. We make marketing software, video series, and educational content based on the belief that anyone can use video to grow their business and their brand.”

Creating sales enablement material
Sales enablement is a crucial function in any product marketing organization. According to Future Market Insights, the global Sales Enablement market is expected to reach $ 6380.1 million in 2025. This will exponentially rise in the coming years due to automation, AI, and digitization. Effective sales enablement materials can bridge the knowledge gap between cross-functional teams, help close more deals, engage prospects, and deliver great outcomes for the business.
Top sales enablement assets
Case studies
Case studies demonstrate quantifiable results and return on investment (ROI). It highlights certain business challenges, solutions, and strategies to avoid such occurrences in the future. It also displays customer testimonials that add value to the business.
Sales script
A sales script is a document that highlights key talking points and common objections for salespeople. It guides sales reps to benefit-driven communication and handling objections. It helps a less experienced salesperson to be more confident by providing distinct customer contexts and calls to action.
Product demos
These showcase the significance of a product through features and operation. It addresses customer needs and drives deeper engagement.
Sales one-pagers
These are carefully pointed and creatively drafted summaries of a product or services. It serves as a quick reference guide (highlighting core value propositions) for potential customers.
Product sheets
These are in-depth datasheets that capture the specifications and capabilities of a product or service. These are vital for technical evaluation and research.
Product comparison charts
These give head-to-head comparisons of a product against its competitors. It justifies a product’s value by addressing potential objections.
Product roadmap assets
This document states a company’s future plans and vision. It reassures prospects about their investment. Product roadmap sheets establish credibility in the company’s direction.

Building customer personas
It is a data-driven profile of the ideal buyer. It represents key traits, such as demographics, values, behaviors, pain points, and goals, enabling businesses to understand who they’re targeting and how to connect with them effectively. By developing personas, companies shift from a product-focused mindset to a customer-centric approach, crafting messages that speak directly to their audience’s needs and preferences.
Creating a persona starts with analyzing current customer data, conducting surveys or interviews, and identifying behavioral patterns. From there, businesses build detailed profiles—assigning names, roles, challenges, and motivations. These personas go beyond basic data by incorporating media consumption habits, job responsibilities, purchase drivers, and demographic factors such as beliefs and values.
Validating personas through feedback and updating them regularly is crucial, as customer expectations and market conditions constantly evolve. Once developed, personas can guide marketing strategies, product development, and customer service decisions, ensuring alignment with target audience needs.
Ultimately, customer personas help businesses personalize communication, provide real value, and build stronger customer relationships. This product marketing function serves as a strategic foundation, allowing companies to engage meaningfully with their audience and improve overall customer experience.

Market research
This branch merges customer behavior with economic trends to refine the business. Market research collects population data, including age, interests, etc., which is relevant to the business. This data helps to spot growth opportunities and address limitations.
The market can easily be understood by evaluating demand, market size, market saturation, pricing, location, etc. It is about knowing your people—the customers. What do they want? What do they need? What keeps them scrolling, clicking, or walking away? It gives a clear picture through surveys, interviews, data analysis, and competitor studies.
Market research validates ideas before investing time and resources. It helps understand if there’s a demand, what features matter most, and how to position your offering uniquely.
Research reveals who your competitors are, what they’re doing well (or wrong), and where your brand can shine. It defines a niche, fine-tunes messaging, and chooses the right platforms to connect with audiences.
There are two main types:
- Primary research (direct information from customer perspective), and
- Secondary research (existing reports, studies, and stats).
Both offer golden insights—especially when combined with qualitative (the “why”) and quantitative (the “what”) data.
Market research is essential in product marketing. It keeps the product relevant, strategy sharp, and the brand one step ahead.
Website management
A website builds the immediate impression of a product or solution. Effective website management is crucial for product marketing.
Think of your website as a 24/7 storefront. Whether someone discovers your product through social media, a search engine, or word of mouth, their next step is usually a visit to your site. What they find there can either spark interest or shut it down. Clean design, fast loading times, intuitive navigation, and compelling content aren’t just “nice to have”—they’re non-negotiable for conversions.
Website management is about strategy. It starts with making sure the user journey aligns with the marketing funnel. Are your product pages optimized for search? Is the call-to-action clear? Do you have trust signals like reviews, case studies, or social proof? A well-managed website subtly guides users from curiosity to commitment.
Content is another key element in product marketing. From product descriptions and landing pages to blogs and FAQs, your site should educate, engage, and convert. It’s also where you communicate your brand story and product value. Regular content updates boost your SEO, keeping you visible in a sea of competitors.
Then there’s the technical side—site speed, mobile responsiveness, analytics tracking, and data security. These may sound boring, but they’re critical. A slow or buggy website can quietly kill interest before you even realize it.
And let’s not forget testing and iteration. Great marketers don’t “set and forget.” They monitor user behavior, run A/B tests, tweak copy and layouts, and use real-time data to continuously improve performance.

Competitive intelligence
This analysis traces the competitive edge to build a lasting impact. Competitive intelligence recognizes the competition surrounding your product or business line. Evaluate the competitors based on the following traits:
- Market size
- New technologies
- Growth opportunities
- Assets and flaws
- Future scope of refining the business
- Obstacles hindering your progress
- Factors impacting the success rate
It is always good to be strategic in the product marketing. Read our article to explore these 5 AI trends in business to stay competitive.