Product lifecycle management (PLM) is a framework of people, processes, and technology that guides all the stages of product development. These stages start right from design to deployment and apply to all industries. This strategy ensures that every aspect of the product is efficient and effective.
Understanding PLM is crucial for any business to survive and thrive in this competitive world. By implementing product lifecycle management software, companies can streamline product development stages, reduce time-to-market, and enhance collaboration across departments. A well-defined PLM system helps maintain quality standards and facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements.
Product lifecycle management evolution over the years
It all started with computer-aided design in the 1970s! Product lifecycle management has evolved from early engineering tools CAD, CAM, and others during the 1970s and 1980s. Later, these tools were integrated with Supply Chain Management (SCM), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and Customer Relationship Management (CRM). These design software formed Product Data Management (PDM) systems in the 1980s-90s further advanced with additional web and visibility tools. Conversely, PLM was formed by combining design tools with ERP, CRM, and SCM.

PLM can predict the feasibility of a product in varying market conditions. It aims to design a system based on the Internet that supports all the stakeholders in knowing, managing, observing, and using all the product-related information. PLM system includes necessary functions like modeling, document management, etc. It also provides components to ensure the monitoring of products from manufacturing to marketing.
Moreover, PLM enables companies to harness valuable insights from data collected throughout the product lifecycle. These insights can drive innovation and inform strategic decisions that lead to improved customer satisfaction and increased profitability. In an era where agility is key, embracing PLM is beneficial and essential for sustainable growth.
Refer to our post on, how to build a profitable business to learn the step-by-step approach to achieving business success.
Stages of product lifecycle management
The product lifecycle management cycle is composed of five phases.
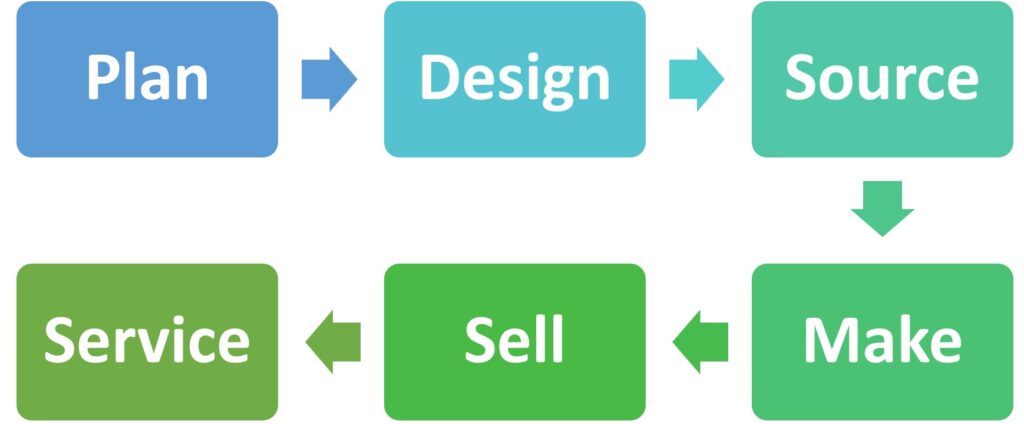
Plan
This stage focuses on identifying the market conditions, selecting the right audience, and developing product strategies. Key activities may include competitor analysis, market research, clarifying product requirements, and setting timelines and budgeting. The planning phase clears the roadmap, business case, and initial specifications.
Read more, explore these 5 AI trends in business to stay competitive.
Design
The design transforms the plan into a physical product structure. It involves concept creation, product architecture, detailed design, prototyping, testing, and Design for manufacturing. The designing phase completes prototypes, design documents, and validation results.
Source
Sourcing identifies and secures the suppliers or materials needed to manufacture the product. It primarily includes Supplier selection, negotiation, Material procurement, Risk management for supply chain issues, and Quality assurance of sourced components. This phase completes contracts with suppliers, locks delivery schedules, and ensures material availability.
Make
Making ensures that the product is manufactured according to design and quality specifications. It involves production planning, manufacturing process setup, quality control and testing, and scaling up production to meet demand. This phase ensures that the finished product is ready for dispatch or distribution.
Sell
The selling phase focuses on distributing and marketing the product in the right market. The core functions include:
- Marketing and promotions
- Distribution and logistics setup
- Sales strategies and partnerships
- Customer acquisition and support
This phase allows product availability in stores or online and customer acquisition.
Service
Service supports customers post-sale and ensures product longevity. It involves:
- Customer service and technical support
- Maintenance, repairs, and updates
- Managing product returns or recalls
- Gathering feedback for future improvements
Service guarantees customer satisfaction, loyalty, and insights for product evolution.
This cycle is iterative, with feedback from each stage influencing future product development and updates.
Requirements of product lifecycle management
The fundamental objective of the PLM system is to respond to a customer’s request to make a good quality custom product. PLM should support the following core functions:
Product data management
It is the basis of product lifecycle management. Companies can ensure data consistency and facilitate effective data exchange and transfer across various application modules through PDM. Handling numerous files was challenging in the early stages of 2D CAD systems. The rise of 3D CAD systems further complicated the management of product information stored in multiple CAD files. To address this issue, Product Data Management (PDM) systems were developed to enable secure check-in and check-out processes from a centralized vault.

PDM systems evolved to track relationships between parts and assemblies and prevent concurrent access to the same files by multiple users. PDM acts as a foundational element of PLM by managing intellectual asset information and their interconnections. While PDM primarily focuses on vaulting, tracking, and managing design files, PLM contains a broader scope of activities such as asset creation through CAD, analysis, digital manufacturing, documentation, and software management.
Also read, 3D printing: The Next Big Trend in Manufacturing.
Development of relationship between company and consumer
Product lifecycle management system caters to the particular needs of each customer. To accomplish this, businesses and consumers must establish relationships by collaboration to reach mutual understanding and develop solutions.
Quality requirement
Customer demand is mostly impacted by product quality. Implementing a quality strategy is an effective measure of enhancing product quality and reducing costs.
Benefits of product lifecycle management
Improved efficiency
Effective product lifecycle management strategies are crucial for businesses to thrive in the current landscape. One of the most substantial advantages of PLM is improved efficiency across all stages of product development. By streamlining processes and integrating systems, companies can reduce redundancies and ensure that teams work cohesively towards common goals.
Learn more about how to set and track smart goals.
Profit margins
Cost reduction strategies ingrained in PLM practices allow companies to identify wasteful expenses and optimize resource allocation. This means that businesses can invest more wisely, ultimately leading to higher profit margins without sacrificing quality.
Enhanced collaboration
Cross-functional teams can communicate seamlessly, share insights, and make informed decisions quickly with effective PLM systems. This collaborative environment nurtures innovation and creativity, enabling teams to respond rapidly to market changes.
Faster time-to-market
It is essential for staying ahead of competitors. Companies can accelerate product development cycles without compromising quality or compliance standards by adopting vital PLM strategies. This agility enhances customer satisfaction and positions businesses as leaders in their respective industries.
Better quality control
It becomes achievable through systematic monitoring and evaluation throughout the product lifecycle. By implementing strict quality checks at every stage—from conception through design to production—companies can ensure that their products meet the highest standards before they reach consumers.
Also read, 15 most valuable terms to understand ISO 9001:2015.
How to choose the right product lifecycle management solution
Scalability
Scalability in PLM systems is essential. According to the business expansion, PLM solution should be able to adapt without requiring a complete overhaul. It’s necessary to look for tools that offer modular features that can expand with varying needs, ensuring long-term viability.
User-friendly interface
Another important aspect is the user-friendly interface of the software selection. A complex system can lead to frustration and decreased productivity among team members. One should always opt for PLM solutions that prioritize usability, enabling all users—from engineers to marketing teams—to navigate effortlessly.

Implementation support services
A robust support structure will ease the transition and provide ongoing assistance to integrate the new system into the workflow. Choosing a provider that offers comprehensive training and support can make all the difference in maximizing the benefits of a chosen PLM tool.
By carefully evaluating these criteria you’ll be well-equipped to select a PLM solution that meets the current needs and positions the business for future growth and innovation.