A profitable business generates more revenue than it spends on expenses, resulting in a net income. Profitability measures a business’s success and sustainability, indicating its ability to create value for its owners and stakeholders. Such corporations often employ effective strategies to manage costs, attract customers, and drive revenue growth. They also adapt to changing market conditions and innovate to stay competitive.
- How to start a profitable business?
- Legal Structure and Registration
- Secure Funding
- Build Brand
- Develop Product or Service
- Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Build a Strong Online Presence
- Focus on Customer Service
- Monitor Financial Performance
- What are the profitable business models?
- Vital factors for business profitability
- Profitable business trends in 2024
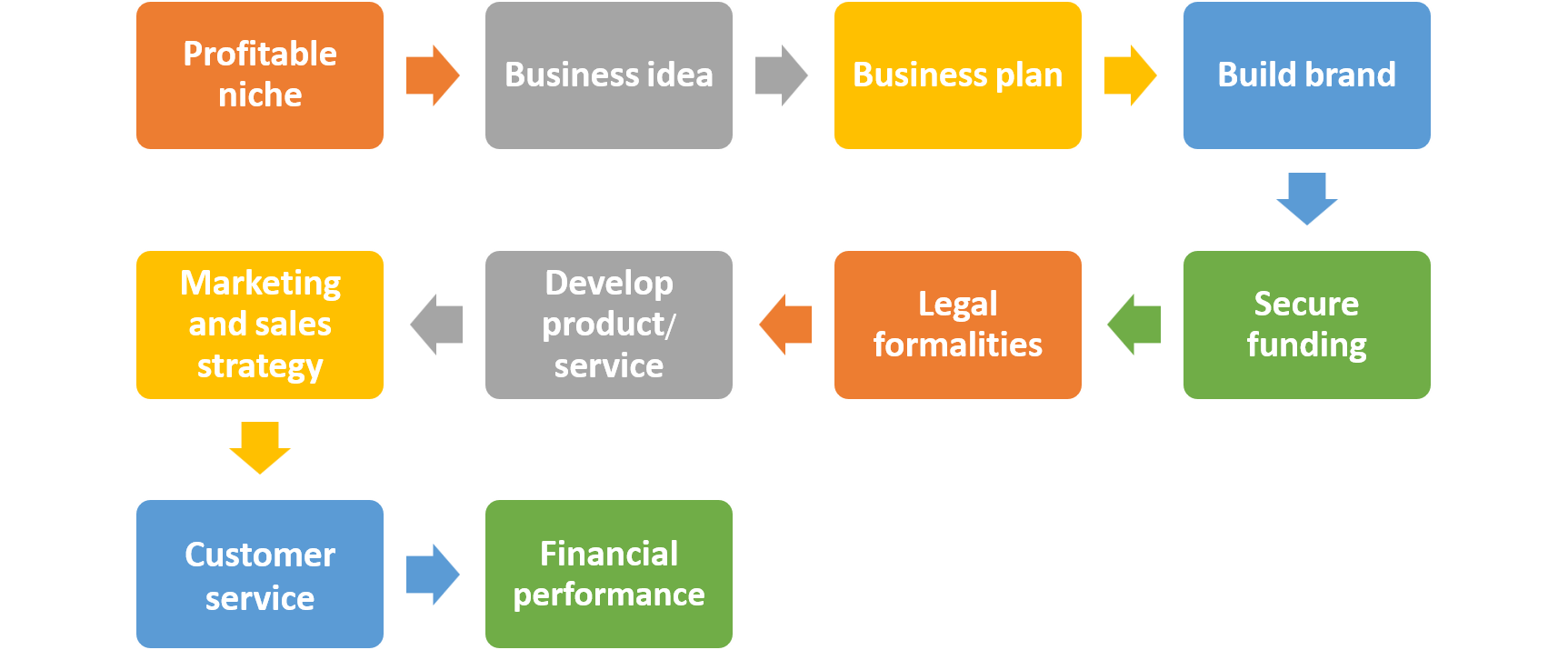
How to start a profitable business?
Starting a profitable business involves careful planning, market research, and execution. Here is a step-by-step guide:
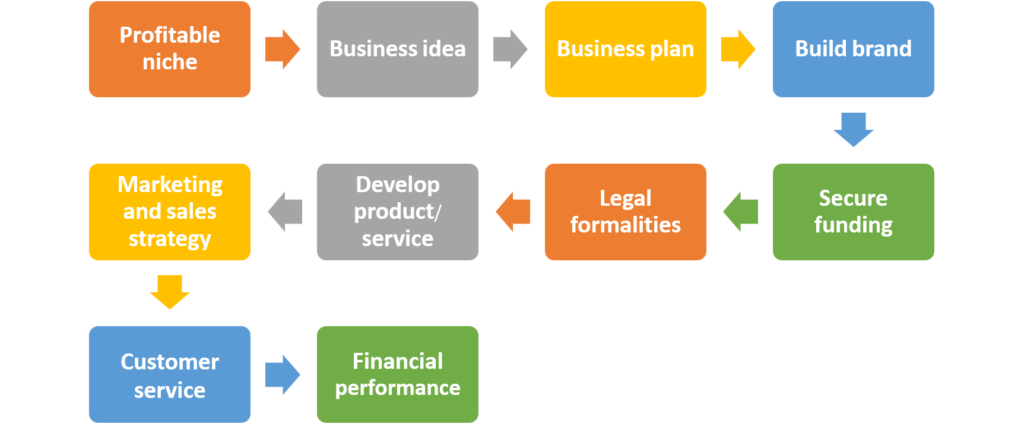
Identify a Profitable Niche
It is crucial for a successful business. Here are some steps to recognize a profitable niche:
- Begin with a list of interests, hobbies, and skills. Consider areas of expertise or passion, as this can sustain motivation and engagement in work.
- Research the market to find areas with high demand and low competition. Look for niches where there is a gap in the market that can be addressed with your products or services.
- Consider the profitability of different niches by analyzing factors such as the potential for high margins, recurring revenue, and scalability.
- Learn the requirements, priorities, and purchasing choices of the target audience.
- Study competitors to know their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. Notice ways to differentiate your business and offer unique value to customers. It is possible to expand business with SWOT analysis.
- Consider Trends and Industry Growth
- Test the idea by conducting market research, surveys, or focus groups to gather feedback from potential customers. It will validate the products/services demand before investing significant time and resources.
- Think about starting small and testing niche ideas on a small scale before committing to a full-scale business.
Read more, 9 ways to choose the right market for your business expansion.
Develop a Business Idea
Developing a business idea involves a combination of creativity, research, and strategic thinking.
- Identify Passion and Skills as this can be a guiding source toward a business idea aligning with strengths and interests.
- Research Market Trends and Opportunities: Conduct market research to identify trends, gaps, and opportunities in the market. Look for areas where there is high demand but low competition, or where one can offer a unique solution to a common problem.
- Evaluate each idea based on criteria such as market demand, competition, scalability, and profitability.
- Develop a Value Proposition: A strong value proposition will help differentiate businesses from competitors.
- Create a Business Plan: Develop a detailed business plan that outlines the business idea, target market, competitive analysis, marketing and sales strategy, and financial projections. A well-thought-out plan will serve as a roadmap for business and attract investors or lenders.
- Test Idea: Before fully committing to the business idea, test it on a small scale to gauge interest and gather feedback. This could involve launching a pilot program, conducting surveys, or hosting focus groups.
- Iterate and Refine.
- Seek Feedback and Advice: This insight can help refine the idea and make it more successful.
Learn more, how to develop Agile business.
Create a profitable business plan

- Executive Summary: Provide an overview of the business idea, highlighting key points such as target market, unique selling proposition (USP), and financial goals.
- Business Description: Describe the business in detail, including its mission, vision, and objectives.
- Market Analysis: Conduct market research to identify the target market, industry trends, and customer needs. Analyze competitors and assess the business’s position in the market.
- Organization and Management: Outline the organizational structure of business, including key roles and responsibilities.
- Product or Service Line: Describe products or services in detail, including their features, benefits, and pricing strategy.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: Outline marketing and sales approach, including target market, promotional tactics, and sales channels.
- Funding Request: Specify the required funding to start or grow the business.
- Financial Projections: Include a detailed financial projection for the business, including income statements, cash flow projections, and a break-even analysis.
- Appendix: Include any additional information that supports the business plan, such as resumes of key team members, market research data, and legal documents.
- Review and Revise: Review the business plan regularly and revise it as needed to reflect changes in the business or market conditions. Update financial projections to ensure they remain accurate and realistic.
Legal Structure and Registration
Choose a legal structure (e.g., sole proprietorship, LLC, corporation) and register business with the appropriate authorities.
Secure Funding
Determine the initial funding needed to start and operate the business. Research alternatives such as loans, personal savings, or investors.
Build Brand
Building a strong business brand is essential for making a positive perception of a company and establishing a loyal customer base.
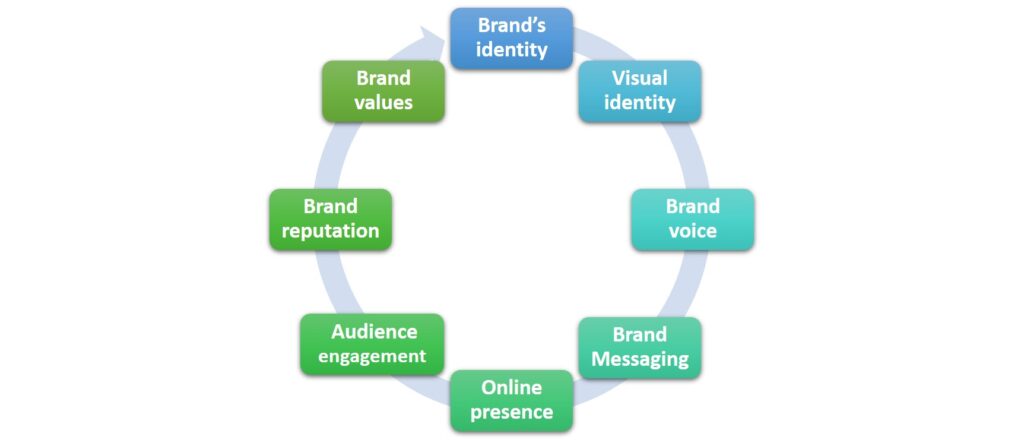
- Define brand identity, including brand values, mission, and personality. Determine what sets the brand apart from competitors.
- Create a Memorable Logo and Visual Identity: Design a logo and visual identity that reflect the brand’s personality and values. Use consistent colors, fonts, and imagery across all branding materials to create a cohesive brand identity.
- Develop Brand Voice including the tone and language used in communications.
- Structure clear and compelling brand messaging that communicates the brand’s value proposition and resonates with the target audience.
- Build a Strong Online Presence.
- Engage with the Audience through social media, email marketing, and other channels. Respond to comments and messages, and listen to feedback to improve the brand’s reputation.
- Monitor Brand Reputation reputation online and address any negative feedback or reviews instantly. Building a positive brand reputation takes time and effort, so be patient and consistent.
- Stay True to Brand Values.
Develop Product or Service
Design a high-quality product or service that meets customer needs and delivers value.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Devise a marketing plan to grow the business and attract customers. Utilize online and offline marketing channels to reach the intended audience.
Running a profitable business requires a combination of effective strategies, careful planning, and continuous improvement.
Build a Strong Online Presence
Create a professional website and leverage social media and digital marketing to increase visibility and reach.
Focus on Customer Service
Deliver excellent customer service to establish commitment and promote recurring opportunities.
Monitor Financial Performance

- Set Clear Financial Goals including revenue targets, profit margins, or expense reduction goals.
- Use Key Financial Metrics such as revenue growth, gross profit margin, net profit margin, cash flow, and return on investment (ROI).
- Use Financial Statements including income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow. These statements provide valuable insights into financial health and performance.
- Track Expenses closely and identify areas where it is possible to reduce costs or improve efficiency. This can help improve profitability and cash flow.
- Monitor Cash Flow to ensure that enough cash is available to meet financial obligations.
- Compare Actual Performance to Budget: This can help to know variances and take corrective actions if needed.
- Use Financial Ratios to analyze financial performance and compare it to industry benchmarks.
- Seek Professional Advice to check financial performance and make informed financial decisions. Review it regularly and adjust financial strategies as needed.
What are the profitable business models?
There are several profitable business models that entrepreneurs can consider, depending on their industry, target market, and goals. Here are some examples:
E-commerce
Selling products online through a website, marketplace, or social media platform. This model can be highly profitable due to low overhead costs and the ability to reach a global audience.
Subscription-based
Offering products or services on a recurring subscription basis. This model can provide a predictable revenue stream and strong customer loyalty.
Freemium
Offering a basic version of a product or service for free, with premium features available for a fee. This model can attract a large user base and generate revenue from upgrades.
Marketplace
Creating a platform that connects buyers and sellers, paying each transaction a commission or fee. This model can scale quickly and generate revenue from a large number of transactions.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Providing software applications on a subscription basis, typically hosted in the cloud. This model can be highly profitable due to recurring revenue and low distribution costs.
Affiliate Marketing
Promoting products or services from other companies and earning a commission for each sale or lead generated. This model can be profitable with the right audience and marketing strategy.
Franchise
Licensing a successful business model and brand to franchisees in exchange for upfront fees and ongoing royalties. This model can be profitable with a proven concept and strong brand.
Consulting and Coaching
Offering expertise and advice to individuals or businesses for a fee. This model can be profitable with specialized knowledge and a strong reputation.
Manufacturing and Distribution
Producing and selling physical products through wholesale or retail channels. This model can be profitable with efficient operations and effective supply chain management.
Digital Products
Creating and selling digital products such as eBooks, online courses, or software. This model can be profitable with low production costs and high demand for digital content.
These are just a few examples of profitable business models. The key is to choose a model that aligns with strengths, interests, and market opportunities, and to continually innovate and adapt to changing market conditions.
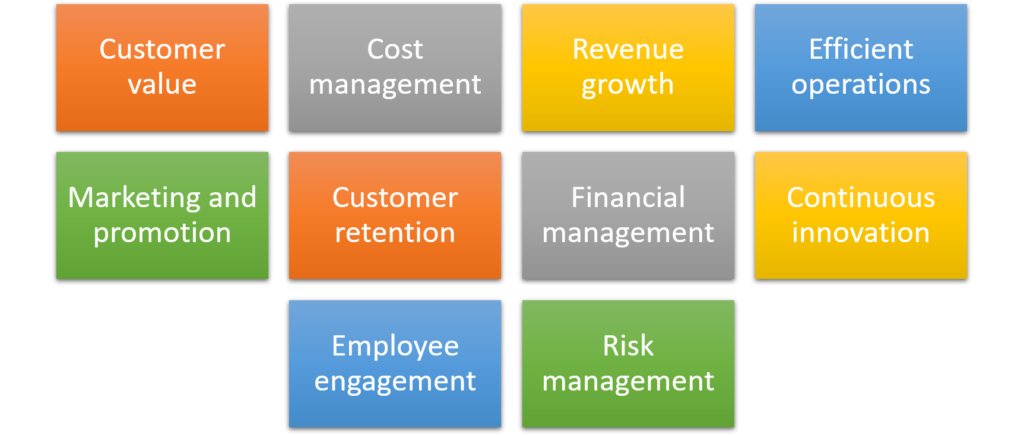
Vital factors for business profitability

- Strong Value Proposition: Offering products or services that provide clear value to customers and differentiate a business from competitors.
- Effective Cost Management: Keeping operating costs low through efficient processes, strategic sourcing, and effective use of resources.
- Revenue Growth: Increasing sales through market expansion, product diversification, or improved marketing and sales strategies.
- Customer Retention: Building long-term relationships with customers through exceptional service, loyalty programs, and personalized experiences.
- Optimized Pricing Strategy: Setting prices that reflect the value of products or services while remaining competitive in the market.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining business operations to reduce waste, improve productivity, and maximize resources.
- Financial Management: Monitoring cash flow, managing debt, and making informed financial decisions to ensure the business remains solvent and profitable.
- Innovation and Adaptability: Continuously innovating products, services, and processes to meet changing customer needs and market trends.
- Effective Marketing and Sales: Implementing targeted marketing campaigns and sales strategies to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
- Talent Management: Recruiting, developing, and retaining talented employees who are committed to the success of the business.
Profitable business trends in 2024
Technology and Software Development
With continued technological advancements, businesses that focus on software development, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and digital transformation are likely to remain in high demand.
E-commerce and Online Retail
The growth of online shopping is expected to continue, offering business opportunities in e-commerce, digital marketing, and logistics.
Healthcare and Wellness
As the healthcare industry evolves, businesses in telemedicine, digital health, wellness products, and services are expected to be profitable.
Renewable Energy and Sustainability
With increasing focus on sustainability and environmental conservation, businesses in renewable energy, recycling, and green technology are likely to be profitable.
Education and E-learning
The demand for online education and e-learning platforms is expected to grow, presenting opportunities for businesses in this sector.
Food and Beverage Industry
Businesses offering innovative and sustainable food products, as well as those focusing on health and wellness trends, are expected to be profitable.
Real Estate and Property Development
Despite market fluctuations, real estate remains a profitable sector, especially for businesses focusing on sustainable and affordable housing solutions.
Financial Services
Businesses in fintech, digital banking, and financial technology are expected to be profitable as the financial industry continues to innovate.
Entertainment and Media
With the rise of streaming services and digital content, businesses in entertainment, gaming, and digital media are expected to be profitable.
Logistics and Transportation
With the growth of e-commerce and global trade, businesses in logistics, supply chain management, and transportation are likely to be profitable.
Entrepreneurs need to conduct thorough market research and analysis to identify specific opportunities within these sectors and develop strategies to capitalize on them.