Compliance with industrial standards, such as ISO 9001:2015, is a mandatory requirement for products, processes, and services. Various industries require ISO certification, including manufacturing, food, energy, medicine, semiconductor, etc. This standard is a crucial aspect of Six Sigma companies. Even though ISO sounds simple, it has a vast vocabulary that consists of different concepts.
This article will highlight a checklist of 15 terms and definitions used in ISO-certified organizations.
A quick glance at ISO 9001:2015
ISO 9001:2015 is a technical standard for the quality management system (QMS) defined by the International organization for standardization (ISO). This standard contains seven principles for enhancing the performance of an organization including:
- Process approach
- Customer focus
- Relationship management
- People engagement
- Leadership
- Improvement
- Decision-making
These elements determine the expertise as well as flaws in the entire system. The purpose is to meet customer and regulatory demands regarding products, individuals, services, testing, etc. ISO certification is an assurance of getting high-quality products and services. Compliance with ISO helps businesses and companies develop 1000x faster.
ISO 9001:2015 aids in developing, executing, and improving the process approach to attain the ultimate goal of customer satisfaction. An understanding and management of cross-functional processes are essential to adopting this standard. PDCA (plan-do-check-act) and risk-based thinking are two popular methods to improve a firm’s productivity.
Read more, how to set and track Smart goals.
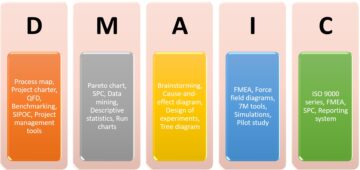
PDCA
This is the fundamental aspect of ISO 9001:2015. It is a four-step model to carry out the improvement.
Plan: Recognize opportunities and make changes accordingly.
Do: Make the change and test it. Perform a small-scale analysis.
Check: Evaluate your test results, analyze the data, and identify what you learned.
Act: Use what you learned during the study step to take action. Retry the cycle if the change does not work. Apply the learnings from the test to wider changes if you were successful. Planning new improvements using what you learned is a good way to restart the cycle.

List of common terminology
ISO 9001:2015 uses the following terminology as a basis for its standardization.
Quality
Quality is the sum of all the attributes and elements of a product or service that specify its ability to fulfill the needs of its users. It is the valuation related to the objective. It is the quality or lack of quality of any product, service, experience, or asset that determines its value. The concept of quality includes both definite properties such as characteristics and indefinite traits such as taste.
Basically, it is an assessment of a specific item’s quality. Technically speaking, it is conformance to requirements. For better understanding, consider a few examples such as product quality, service quality, or quality of life.
Quality control (QC)
It is a part of QMS that refers to fulfilling the quality demands of a particular product. QC focuses on testing and inspection.
Quality assurance (QA)
It is also a part of QMS that gives assurance of meeting the quality requirements. QA is a tool that enhances quality processes to achieve intended results. It considers internal and external management including agencies, governments, third parties, etc.
Quality management system
In any organization, a quality management system is a collection of policies, procedures, and processes that are used to plan and deliver (production/service/development) products and services. ISO compliance is a must-have attribute.
Process
It is a task of transforming inputs into outputs by utilizing necessary resources.
Sometimes, processes and procedures might sound familiar. But there is a subtle difference between both terms. The process is an activity to convert raw material into finished goods, while the procedure is a set of instructions to carry out the process.
Scope
An area of application that describes the objectives and requirements of the process is known as a scope. Each project or assignment revolves around its Scope. Usually, this is what your project is supposed to accomplish (deliverables). In terms of product scope, it is the core product or instrument to be created and delivered to the customer or end-user.
Inspection
It is a phenomenon that verifies compliance with specific requirements by checking, measuring, or testing the product or service features. Inspection exists primarily in three phases: Pre-process (raw material inspection), in-line, and Post-process. These phases can be divided into various stages according to the requirement analysis.
The inspection involves using and handling various tools, instruments, and software. For instance, calipers, gauges, tapes, cameras, microscopes, etc.
Audit
Auditing is a method of assessing the effectiveness of the QMS for pinpointing risks and verifying adherence to requirements. The effectiveness of the audit depends on the collection of specific evidence. In the event of non-conformity, corrective and preventive action is taken.
Generally, audits are conducted after particular planned intervals, also known as internal audits. This amazing approach to auditing allows you to document planning, execution, completion, NCs, etc.

Conformity vs Non-conformity
Conformity in ISO 9001 is adherence to specific standards or rules, while non-conformity is a deviation from a specific norm. Simply put, non-conformity is a process that fails to accomplish the intended purpose. On the other hand, conformity brings out the expected result.
Defect
A defect is a type of imperfection or fault caused due to man, machine, material, and environment. Here are some important reasons:
- Process disorder
- Lack of proper planning, resources, or services
- Inappropriate analysis of customer demands
- Wrong setup/calibration/technology
- Material shortage
- Variation due to design or manufacturing errors
- Miscommunication
- Absence of vision and mission
- Humid factory settings
These are the few categories causing errors.
Error-free products can be produced by using various quality tools like Kanban, Kaizen, 5S, etc.
Standards
A standard is a collection of practices, methods, systems, conditions, or specifications set by industry advisory groups that assist manufacturers in performing and sustaining product quality consistency.
Improvement
In an organization, quality improvement refers to unrelenting efforts put in by everyone to enhance every aspect of their work, especially the vital processes. It is an organized strategy of erasing or reducing rework, scrap, and defeats in production.
Continuous improvement in ISO 9001:2015
Kaizen, or continuous improvement, refers to finding ways for streamlining work and reducing waste. Industries are implementing various tools such as PDCA, root cause analysis, lean methodology, and many others. Continuous improvements are made in the development of services, products related to services, and products under development. This also applies to the established and implemented processes.
Continual improvement
This approach is replicated and paused between repetitions to accomplish continuous improvement. In this system, improvements are made in phases, followed by a break to evaluate and analyze the results, then improvements are made again.
Continual improvement aims to improve existing systems to get better results. Whereas continuous improvement is a chain link to continual that emphasizes short/little modifications within a system rather than huge advancements.
Compliance
It is an act of adhering or conforming to specified rules, regulations, or policies.
Efficiency vs effectiveness
These two terms often create confusion while working with ISO 9001. Efficiency is a way to determine how well resources are used to acquire a particular outcome. In simple terms, it is the ratio of input to output.
KPIs (key performance indicators) are defined to measure the success rate of any process. For efficiency, KPIs are:
- Productivity
- Energy expense per yield
- Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE)
Effectiveness relates to the extent to which scheduled actions are completed, and intended outcomes are reached.
KPIs of effectiveness consists of:
- Quality rating
- Occurrences of non-compliance per year
- On-time delivery
- High customer satisfaction index
Customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction measures how many clients/customers are delighted with what a firm offers (products or services) while surpassing specified satisfaction objectives. It is crucial for maximizing customer lifetime value, stopping client churn, and assuring good brand orientation.
Corrective action
An appropriate corrective action plan (CAP), known as corrective action, involves taking steps to identify a problem’s root cause and creating a solution to prevent its recurrence by modifying it. The goal is to prevent problems from recurring within an organization by improving its processes. It not only mitigates damage caused by a failure but also corrects the problem permanently.
Preventive action
As the name suggests, preventive action is a method of eliminating causes that could cause danger or undesirable situations. This enables you to fix a problem, risk, or flaw in a system. The organization may also take measures to improve its roadmap or position. Also, a company should have controls to confirm preventive actions are in place and functioning.
Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) can be the better means of identifying corrective actions and taking preventive measures.
Leadership in ISO 9001:2015
Typically, leadership is defined by characteristics, qualities, and conduct. The structure and direction of an organization and the behavior of leaders play a vital role in the effectiveness of a quality management process. Leaders entrust and help employees throughout the organization in their quest for excellence.
The scope of ISO 9001:2015 is wide with multiple terminologies. Please write to us in the comment section if you have any suggestions.

Excellent… But could you please elaborate PDCA under ISO article?
Done! Thank you for your suggestion!
[…] Lithography, Baking, Etching, Doping, Metal deposition, and Wafer formation. According to ISO 14644-1, cleanrooms belonging to class 100 are recommended for such production. A cleanroom is an […]
[…] lives. There are several authorized standards for vehicle design, safety, service, and maintenance. ISO 26262 compliance focuses on automotive functional safety. But self-driving cars go way beyond […]
[…] to our article on the 15 most valuable terms to understand ISO 9001:2015 to understand industry compliance and optimize the […]
[…] Also read, the 15 most valuable terms to understand ISO 9001:2015. […]
[…] is mandatory to follow ISO 9001:2015 to ensure defect-free production and optimization of the […]
[…] ISO 9000 series of international standards provide a framework for companies to document the quality system […]
[…] Refer to our article, 15 most valuable terms to understand ISO 9001:2015. […]
[…] If you want to learn more about the quality of products, refer to the 15 most valuable terms to understand ISO 9001:2015. […]
[…] to our article about the 15 most valuable terms to understand ISO 9001:2015 to know the industrial quality […]