Industry 4.0 is the fourth industrial revolution driven by the Internet of Things (IoT), the latest trends, and technologies. It combines digital, virtual, and intelligent performance to build advanced manufacturing technology models. The industrial revolution began with the first stage, then the second, followed by the third, and now we are witnessing the fourth one.
We have briefed about IIoT (Industrial internet of things) in the article top 5 IoT application domains. This one will cover the trends and principles of Industry 4.0.
What is industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is a new model that integrates the cores of the last three revolutions and utilizes digitization, virtualization, and intelligent techniques. It has advanced capabilities for all stages, from the product inception to the final delivery to the customer. This term was first coined in 2011 by the German Government. It was mentioned as the integration of automation with IT.
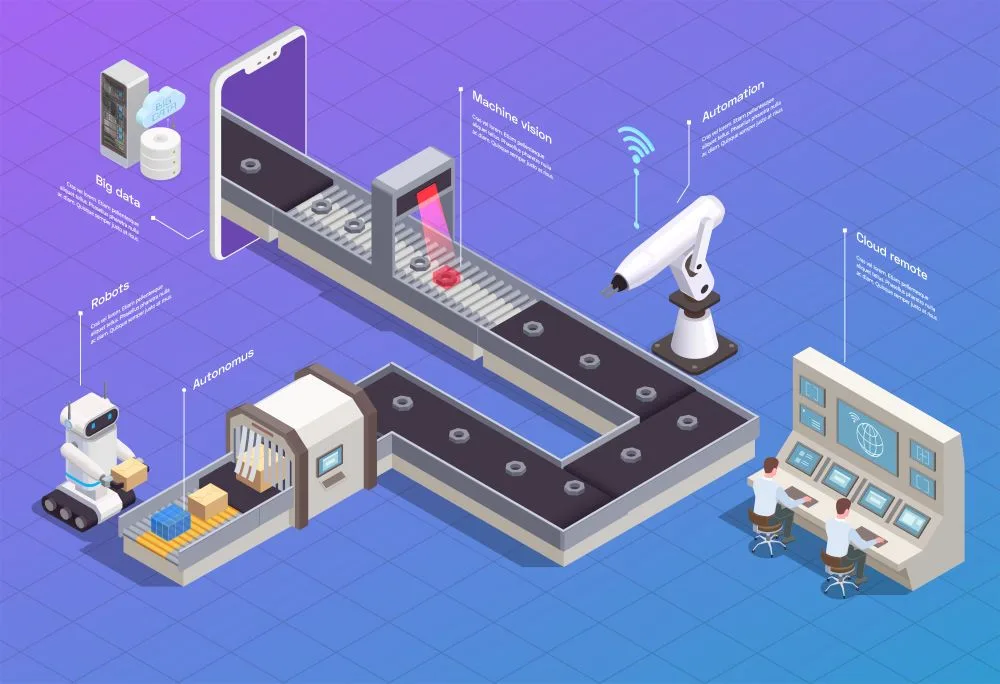
Industry 4.0 establishes the following:
- Configuration and management of smart production according to the requirement.
- Easy reconfiguration of production for fulfilling particular customer demands and controlling all the stages of production.
- Product lifecycle management (PLM)
These things coordinate and form intelligent factories, logistics, and production.
This process includes three fundamental aspects: knowledge for understanding, discoveries through experimentation, and innovation. These aspects were the same in all the revolutions. Let’s just quickly go through the evolution history.
First revolution
The first industrial revolution began in mid 18th century and lasted till the 19th century. The Discovery/formation of the steam engine was the greatest innovation in this period. The expansion of production activities, business logic, utilization of railways, telegraphs, navigation systems, widespread communication, and transportation were the main catalysts of this era.
James Watt, Eli Whitney, and Samuel F. B. Morse were some of the key figures in the first industrial revolution.
Second revolution
This period started during the second half of the 19th century with the creation of steel industries and electricity. It has also developed advances in the oil and chemical fields. In this period, countries like France, Germany, the United States, and the United Kingdom were crucial industrial pioneers. This has also marked the developments in steam-powered ships, aeronautics, refrigeration, consumer goods, food canning, preservation, etc.
A few notable scientists in this era include Thomas Edison, Andrew Carnegie, Sir William Henry Perkin, and James Murray.
Third revolution
This digital era began in the 1970s and developed technologies such as computer science, biotechnology, Computer Numerical Control (CNC), digital electronics, machining processes, microelectronics, telematics integrated systems, etc. This revolution changed the entire view of industrialization and globalization.
Industry 4.0 aspects
Virtualization
It provides tools to assist humans in their work. This focuses on machine-to-machine communication and control. Sensor data is connected to virtual plants and simulation models. The physical world can thus be replicated virtually. Virtualization facilitates decision-making and analysis of the process in real-time.
Modularization
In modular systems, individual production modules can be replaced or expanded to accommodate varying needs to ease attaching or detaching modules. This is best to modify demand fluctuations or to include new techniques. Modularization achieves customer satisfaction, consistent productivity, and error-free products.
It is mandatory to follow ISO 9001:2015 to ensure defect-free production and optimization of the process.
Service adaptation
It is the availability tracking of manpower, services, or products through the Internet. The aim of this adaptation is to assist stakeholders with product service. With Industry 4.0, collaborations with all stakeholders remain strong, whether they are customers, partner industries, or suppliers. With virtual and digital platforms available round-the-clock, anyone can obtain information about the industry, services, and products.
Read more about how to convert small and medium scale enterprises into industry 4.0.
Interoperability
In simple words, interoperability means controlling the operations of other functions connected through software and programs. A smart facility with intelligent machines and storage systems can drive actions, exchange information, and control the whole operation. This process also facilitates the cooperative relationship between machines and humans.
Refer to our article on 5 amazing smart cities and their components.
Decentralization
Decentralization gives decision-making authority to an individual person or machines associated with a specific work function. This eliminates the hold of centralized bodies that were reviewing or approving decisions. Shopfloor operators, machines, or specific responsible individuals can make decisions that will positively impact the process or the company. This is a flexible approach that uses individual expertise and yields better results in a short duration.
For instance, consider banks and blockchain technology. The bank acts as a centralized body that keeps an eye on all the activities. On the other hand, a blockchain is a decentralized network where people can handle and monitor their accounts.

Real-time capability
Real-time capability refers to the ability of intelligent machines to adapt the manufacturing process with specific software and make decisions according to the requirements. Thus, resource misuse and material waste are reduced, while energy efficiency is improved. This ensures that the industry will respond to internal and external stimuli in a timely manner by communicating, acquiring, and examining data in real-time.
Trends in Industry 4.0
Refer to the below information about the latest techniques in Industry 4.0.
IoT
It is a distributed mesh of interconnected physical things equipped with actuators, sensors, software, and other techniques for relating and sharing data with other machines through the network. It stores large amounts of data in the cloud computing system.
IoT increases efficiency, reduces waste, establishes communication between all the systems, enhances work, and results in prompt customer delivery.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence, or AI, is the study of creating technology capable of making autonomous decisions and taking action on its own. It includes reasoning, problem-solving, language understanding, perception, and learning without human aid. This drives innovations and advances in several fields such as manufacturing, retail, logistics, supply chain, etc. To facilitate working, AI employs certain branches like machine learning, fuzzy logic, robotics, etc.
For example, consider self-driving cars that drive smoothly, cross obstructions, and pay attention to traffic signals without human intervention.
Augmented reality
Augmented reality combines the physical world with virtual data using multimedia, intelligent interaction, 3D modeling, and other things. Digital systems related to cameras, GPS, 3D scales, and algorithms facilitate the connection of reality with digital simulation. These tools enable humans to perform duties more efficiently by supplying appropriate information. Furthermore, it is vital to position the algorithm and camera correctly for an accurate examination of the object. It fixes errors instantly and saves a lot of time.
5G
With high-speed, low-latency, less congestion, and tight security, the 5G network is booming. This extremely reliable network will promote industrial control, cyber health, smart application management, surveillance systems, and so on. 5G technology will streamline manufacturers’ end-to-end operations and allow them to add or eliminate virtually new product lines or entire factories. Manufacturers can achieve huge productivity gains through the deployment of billions of sensors, programmable robots, and autonomous logistics, which can all communicate and operate remotely through 5G. Evolution and transformation will happen in many industries thanks to 5G, contributing directly to social and financial advancement.
Cybersecurity
It is a process of shielding computers, programs, networks, and additional sorts of data from digital attacks. Cybersecurity protects data confidentiality, availability, and integration. It can be achieved with encryption, cloud computing, web servers, and IPV6 (new internet protocol).
Mitigation of cybercrimes is a fundamental requirement of this intelligent industry 4.0.

Big data
As the name suggests, big data is a huge portion of structured, unstructured, and semistructured information that is hard to manage and control. This data helps companies to form big decisions related to their economy. This also includes weblogs, sensor data, social network information, marketing campaigns, etc.
An idea or a consideration can be induced by the user about information that the company was clueless, about and the chance to acquire external information that was unavailable before, such as comments (or likes) on social networks. With all this well-organized data, industry 4.0 is able to predict and solve problems before they arise or determine trends that will benefit the organization’s economic growth.
Additive manufacturing
The process of additive manufacturing is the creation of intricate parts by adding layers over time based on 3D CAD models. Additive manufacturing describes a set of techniques that enable the 3D printing of physical objects.

As a result of this process, a user can deliver customized designs to clients that were once unimaginable. Customers can order according to their preferences, and Industry 4.0 will handle the entire relevant method to get the final, personalized outcome. Additive manufacturing would also minimize resource consumption and manufacturing expenses. Moreover, it will encourage a zero-waste culture due to customizability without requiring extra means and costs.




[…] implemented in industry 4.0 is popularly known as IIoT (industrial internet of things). IIoT has expanded its scope into a […]
[…] small and medium scale enterprises, popularly known as SMEs, into Industry 4.0 is a challenging task. Such businesses include manpower of fewer than 250 people and thus face […]
[…] concept is leading the Industry 4.0 revolution, leveraging state-of-the-art data analytics and the seamless interconnectivity of the Internet of […]